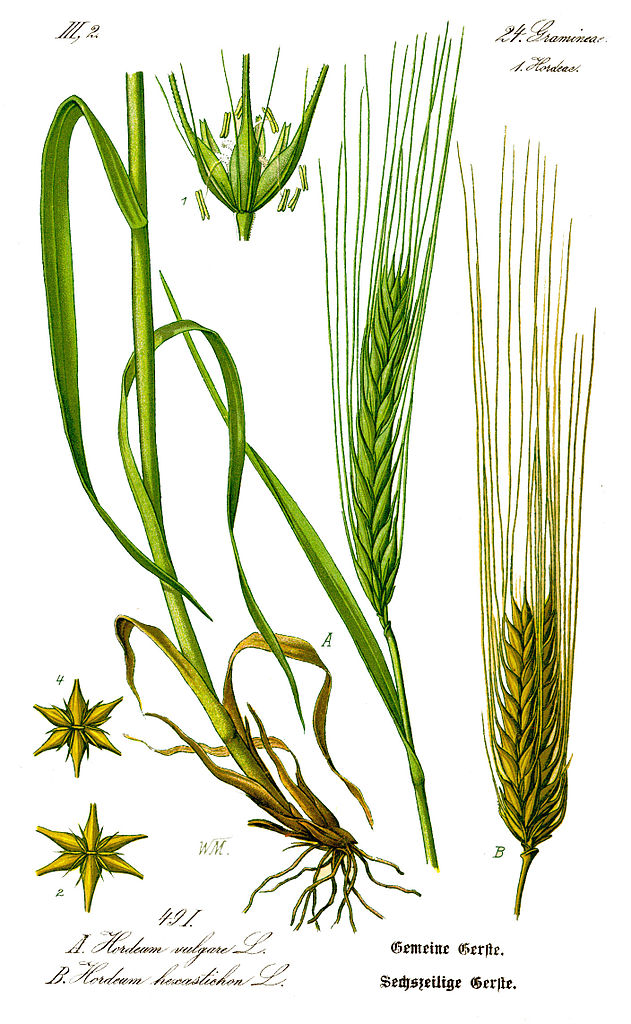
Yava:

Phytochemistry:
Seeds- Cyanogenic glycoside characterized as 2- β-D- glucopyranasyloxy – methyl – (2R) – butyronitrile, ubiquinones,proanthocyanidins, glycosides of hordatines A & B, procyanidin B3, trimer of procyanidin C2, prodelphinidin, chrysoeriol, hordeumin, pangamic acid, protein, carbohydrates, calcium, phosphorus, iron.Leaves- Arabinogalacto (4 - 0 – methyglucurono ) – xylan , cyanogenic glucoside, 6’’ – sinapolysaponarin, 6’’-feruloylsaponarin and 4’ – glucosyl – 6’’ – sinapolysaponarin, 2’’- 0- glycosylisovitexin.
Whole plant- p- coumaroylagmatine, hordenine and its derivative, pyrrolidine, luteolin glycoside, flavones glycosides- orientoside and orientin, cynoglucosides-3- beta- D – glucopyranosyloxy- 2- methylpropene, 4 – beta – D – glucopyranosyloxy – 3- hydroxyl – 3- hydroxymethy- butyrobitrile
PHARMACOLOGY:
IMPORTANT FORMULATIONS1. Yava Kshara
- » Classification and names of Yava
- » Synonyms and definitions of Yava
- » Drug Properties of Yava
- » Chemical Constituents of Yava
- » Standardization of Yava
- » Parts used and Dosage of Yava
- » Morphology and Histology of Yava
- » Distribution and Conservation of Yava
- » Cultivation of Yava
- » Yava in the market
- » Medicinal Uses of Yava
- » Researches and clinical trails of Yava
- » Yavain other sytems of medicine
- » Ayurvedic formulations with Yava
- » Images of Yava