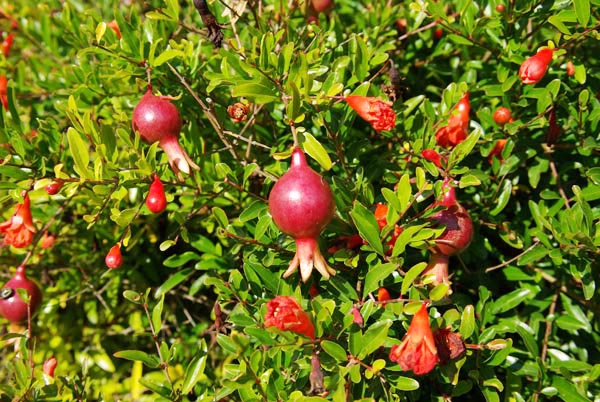
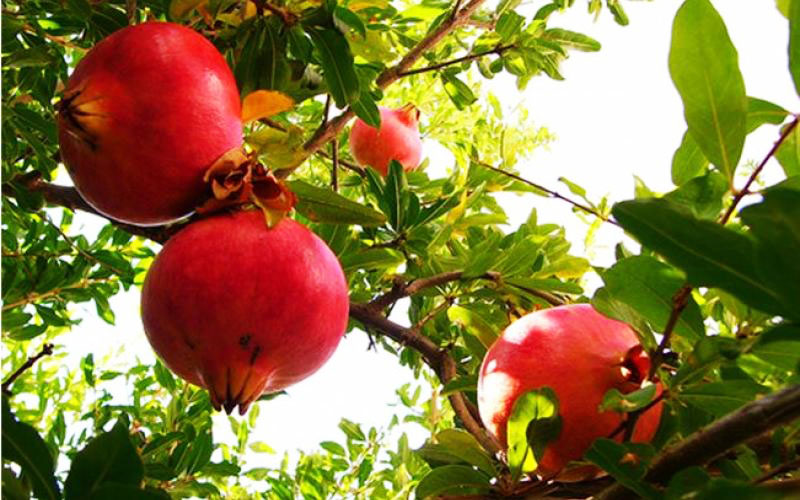
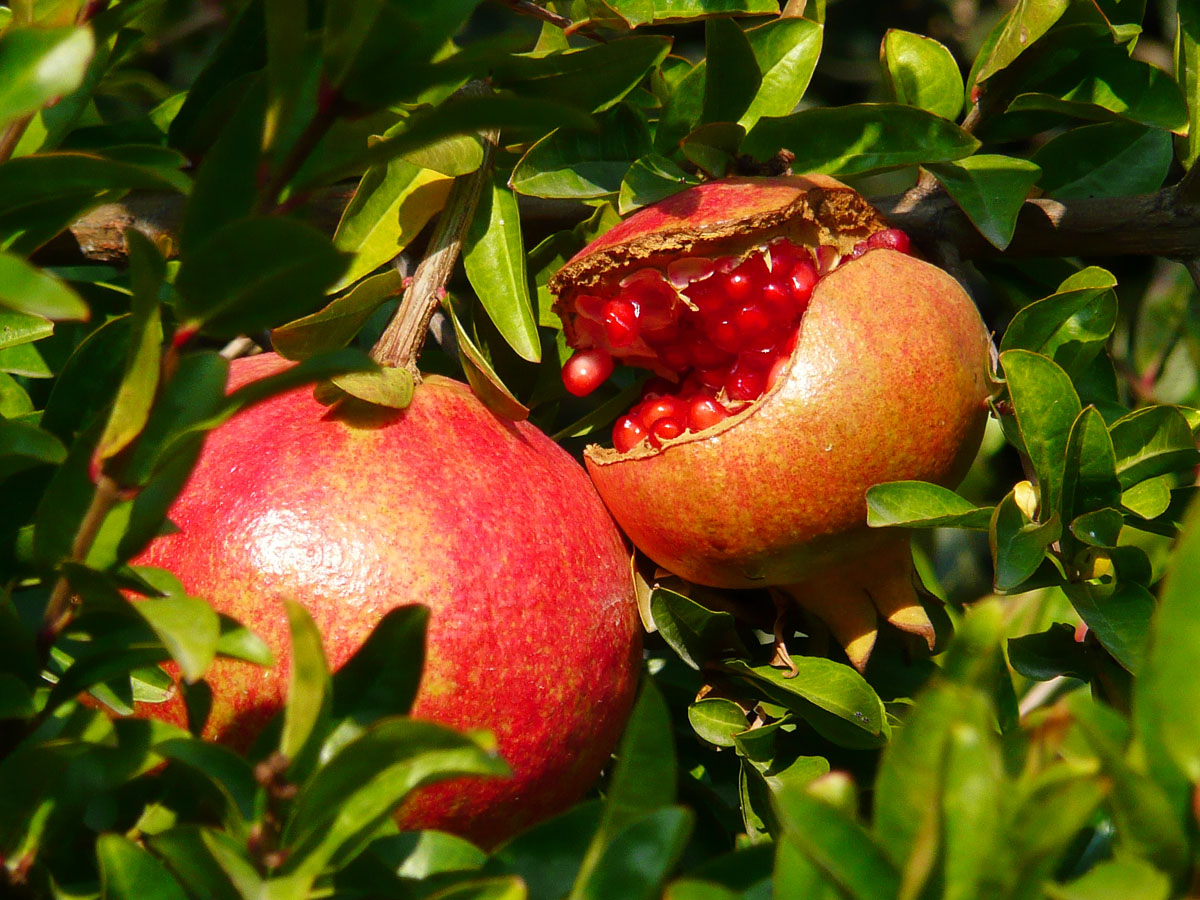
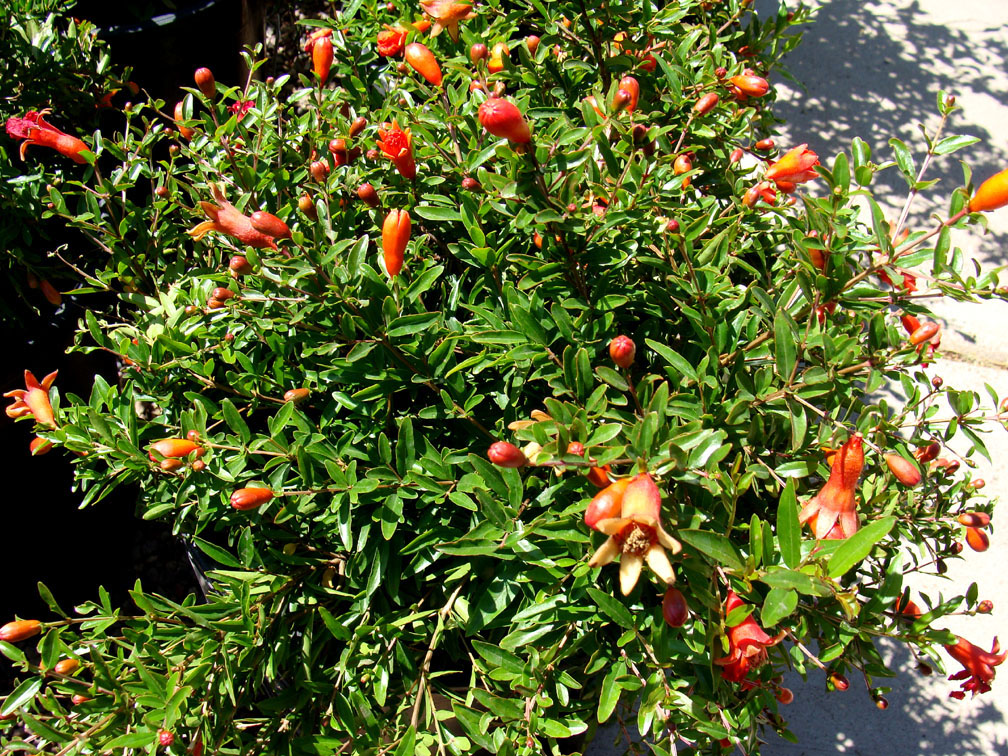
dadima :
 Dadima is one of the herb mentioned in ayurveda. It has been been commomnly used as an edible fruit as well as for medicinal purpose
Dadima is one of the herb mentioned in ayurveda. It has been been commomnly used as an edible fruit as well as for medicinal purposeHISTORICAL AND MYTHOLOGICAL REVIEW:
Pomegranate is native to a region from modern-day Iran to northern India. Pomegranates have been cultivated throughout the Middle East, South Asia, and Mediterranean region for several millennia, and also thrive in the drier climates of California and Arizona.Pomegranates may have been domesticated as early as the 5th millennium BC, as they were one of the first fruit trees to be domesticated in the eastern Mediterranean region.Taxonomical Classification
Kingdom: Plantae - Plants
Subkingdom: Tracheobionta - Vascular plants
Superdivision: Spermatophyta - Seed plants
Division: Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants
Class: Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons
Family: Lythraceae
Genus: Punica
Species: P. granatum
VERNACULAR NAMES
Sanskrit: Dadima ,Lohitapushpa,DantabijaEnglish: pomegranate
Hindi: Anar, Anar-ke-per
Urdu: Anar
Telugu: Dadimbakaya,Dadimma
Bengali: Dadima, Dalim,Dalimgach
Marathi: Dalimba
Oriya: Dalimba
Gujarathi: Dadam, Dadam phala
Tamil: Madulam pazham
Malayalam: Mathalam
Kannada: Dalimba, Dalimbe hannu
Punjabi: anardana
Arabic: gulnar
Spanish: Granada
Assamese: Dalim
Japanese: Zakuro
Chinese: shiliu
French: Grenade
German: Granatapfel
Persian: anar
Tulu: Dalimbe
Greek: Rodia
Varities:
Punica granatumDefinition
Dadima - Fruits are cut openSynonyms
Synonyms in Ayurveda: dadima, dadim, lohitapushpaka, suphala, rocan, shukavalabha, sunil, raktakusum, shukapriya, dashanabij, raktapushpa, pindapushpa, dalima- Dadima : The fruit are cut open
- Karaka : The seeds are scattered
- Dantabeeja : The seeds are like the teeth.
- Lohita pushpa : The flowers are red in colour
- Sukteshtam : It is liked by favourite of parrots
- Kuttima : The fruit which is usually cut open
- Phalashadava : The fruits are sweet or sor in taste
- Raktabeeja : The seeds are red in colour
- Svadvamlam : The taste of fruit is svadu and amla
- Valkalaphala : The fruit is covered with leathery rind
- Pathyakari : It is good for health
- Vrittaphala : The fruits are some what round in shape.
- Vathalaphala : The fruit is covered with leathery rind
- Kuchaphala : The fruits are like the shape of breast.
- Manibeeja : The seeds are like ruby
- Rasalaka : Contains full of juice
- Kumi : Cut to remove the seeds.
- Shukapriya : Dear to parrots
- Rochana : Stimulating taste
Rasa: Amla Kashaya Madhura
Guna: Laghu Snigdha
Veerya: Ushna
Vipaka: Maduram
Karma: Depana Hridya Pachana Pittahara Vatahara
It is one of the extensively used vegetable drug (Phala varga Dravya) in the therapeutics by Brihat trayi. The seeds are used in the treatment of Grahani, Atisara and Pravahika. Fresh juice of it’s flowers will be used as nasal drop in the management of epistaxis(Nasagata Raktapitta).
Cultivation:
The pomegranate is native to the region of Persia and the western Himalayan range, and has been cultivated in India, Iraq, Afghanistan , Pakistan , Iran , Russia, and the Mediterrananean region for several millennia.Pomegranates have been cultivated for centuries for their juicy arils. They are grown in mild temperate to subtropical climates in regions with cool winters and hot summers. Drought tolerant, the trees actually prefer a semi-arid climate, planted in deep, acidic loam with good drainage.
Punica granatum is grown as a fruit crop plant and as ornamental trees and shrubs in parks and gardens. Mutuxe specimens can develop sculptural twisted bark multi trunks & distinctive over all form. Pomegranate and drought tolerate and can be grown in dry areas with either a Mediterranean winter rainfall climate or in summer rainfall climates. In wetter areas, they can be prone to root decay from fungal diseases. They tolerate of moderate frost, down to – 10 deg C (14F).
Propogation:
Dadima is one of the herb mentioned in all ancient Sanskrit scriptures of Ayurveda . It has been commonly used as an edible fruit, as well as for medicinal purpose.Harvesting:
Don’t expect to begin harvesting pomegranate fruit until 3-4 years after planting. Once the trees have reached that age of maturity, the fruit will ripen about 6-7 months after flowering – generally making harvest season for pomegranates in September for early ripening varieties and continues through October for later ripening cultivars.
When harvesting pomegranate fruit, pick when the fruit is fully ripe and a deep red in color since it does not continue to ripe post-harvest. Begin picking pomegranates when the fruit makes a metallic sound when you tap it with your finger.
Phytochemistry:
Fruit peels – Tannin, Punicalin , Punicalagin
Seed – Estrone , Punicic acid
Stem – Malvidin , pentose glucosides, tannin. Ursolic acid.
PHARMACOLOGY:
Relieves morbid thirst
Relieves burning sensations
Anti-febrile
Removes bad odour from stomach, throat and mouth
Nourishing
Promotes semen
Absorbent, binds stools
Brain tonic
Tonic
Builds blood
Antiparasitical
Parts used for medicinal purpose
Bark, Flower, Fruit, Root, ,Dosage:
Fruit juice – 20 – 50 ml
Decoction – 40-80 ml
Rind or bark powder – 3-5 g
Commercial value:
Fruits are of commercial value. Roots are used only for medicinal purpose in Ayurveda.Morphology:
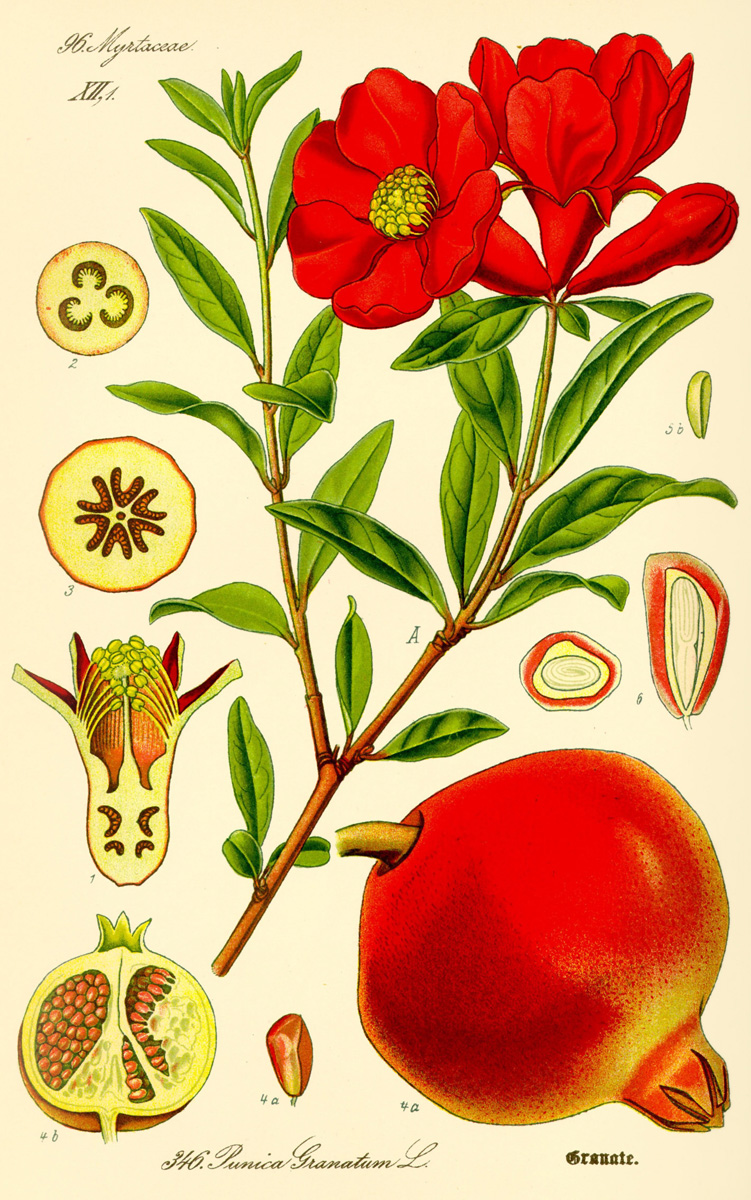
A shrub or small tree growing 5 to 10 m (16 to 33 ft) high. P. granatum leaves are opposite or subopposite, glossy, narrow oblong, entire, 3–7 cm (1.2–2.8 in) long and 2 cm (0.79 in) broad. The flowers are bright red and 3 cm (1.2 in) in diameter, with three to seven petals.Histology:
Red-purple in color, the pomegranate fruit husk has two parts: an outer, hard pericarp, and an inner, spongy mesocarp (white "albedo"), which comprises the fruit inner wall where arils attach. Membranes of the mesocarp are organized as nonsymmetrical chambers that contain seeds inside arils, which are embedded without attachment to the mesocarp.Containing juice, the arils are formed as a thin membrane derived from the epidermal cells of the seeds.The number of seeds in a pomegranate can vary from 200 to about 1,400.
Botanically, the edible fruit is a berry with seeds and pulp produced from the ovary of a single flower.The fruit is intermediate in size between a lemon and a grapefruit, 5–12 cm (2–5 in) in diameter with a rounded shape and thick, reddish husk
Geographical distribution:
- It is found throughout India.
- Wild in north –west region
- Pomegranate is drought-tolerate and can be grown in dry areas with either a Mediterarian winter rainfall climate or in summer rainfall climate.Since ancient times pomegranates have been grown in the Mediterranean region, the Middle East and South Asia
ECOLOGICAL ASPECT:
P. granatum is grown for its fruit crop, and as ornamental trees and shrubs in parks and gardens. Mature specimens can develop sculptural twisted-bark multiple trunks and a distinctive overall form. Pomegranates are drought-tolerant, and can be grown in dry areas with either a Mediterranean winter rainfall climate or in summer rainfall climates. In wetter areas, they can be prone to root decay from fungal diseases. They can be tolerant of moderate frost, down to about −12 °C (10 °F).
Insect pests of the pomegranate can include the pomegranate butterfly Virachola isocrates and the leaf-footed bug Leptoglossus zonatus, and fruit flies and ants are attracted to unharvested ripe fruit
Plant conservation:
Not in conserved listGeneral Use:
It is one of the extensively used vegetable drug (Phala varga Dravya) in the therapeutics by Brihat trayi. The seeds are used in the treatment of Grahani, Atisara and Pravahika. Fresh juice of it’s flowers will be used as nasal drop in the management of epistaxis(Nasagata Raktapitta)Therapeutic Uses:
- Upadamsa – Powder of Bankhuka leaves and Dadima bark may be dusted over the scortum (B.P)
- Arsas – Ghee prepared with Dadima svarasa and Yavaksara will check bleeding and pain(C.S.Ci.14)
- Puyameha – Fruit rind of Dadima is made as infusion and Administered with sugar orally (S.B.M)
- Raktarsas – Dadima bark made into curna and given internally with takra (C.S)
- Aruchi – Dadima svarasa along with saindhava lavana (C.D)
- Bleeding from mouth -Bark made into curna and given withhoney.(H.S)
Clinical trials:
- Punica granatum extract in a dose of 1g orally increased pentabarbitone sleeping time may 27% in rats. The extract provided protection against castor oil induced diarrhea in rats. The relaxant effect was observed on isolated rabbit’s ileum and rat’s uterus ( Annual report, CCRAS 1978 -79).
Fruit skin given along with diet for 4 weeks to rats and guinea pigs showed antifertility effects. (Gujral et.al.1960)
Research:
- Anti bacterial activity of the extracts of bark, fruit, pulp, flowers and leaves is reported (Chopra et.al.1960)
- Antifungal activity of the extracts of bark, fruits, pulp, flowers and leaves is reported (Charya et.al 1979)
- The alcoholic extract showed anthelmentic activity through inhibition of transformation of eggs to filariform larvae of Haemonchus contours (Vishwa prakas et.al 1980)
Precautions:
It causes constipation , hence people with such issues needs to watch out.Toxicity studies:
Non ToxicCONCLUSION:
Pomegranate is a sweet fruit which has very good medicinal and nutritional value and recommended to include in diet for all ages.Photos of dadima -
- Courtesy: Worldwide web
- Courtesy: Worldwide web
- Courtesy: Worldwide web
- Courtesy: Worldwide web
- Courtesy: Worldwide web
KEY WORDS: Pomegranate
- » Classification and names of dadima
- » Synonyms and definitions of dadima
- » Drug Properties of dadima
- » Chemical Constituents of dadima
- » Standardization of dadima
- » Parts used and Dosage of dadima
- » Morphology and Histology of dadima
- » Distribution and Conservation of dadima
- » Cultivation of dadima
- » dadima in the market
- » Medicinal Uses of dadima
- » Researches and clinical trails of dadima
- » dadima in other sytems of medicine
- » Ayurvedic formulations with dadima
- » Images of dadima