sahadevi :
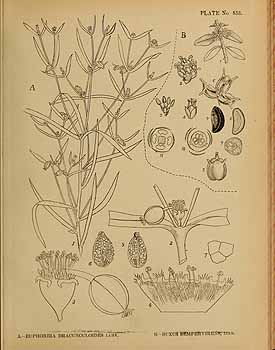
 Dragon Spurge is an annual or short-lived perennial herb, growing to 10-40 cm tall. The species name dracunculoides means resembling a small dragon. Stem, 3-7 mm thick, are sometimes branched from below. Alternately arranged leaves are linearly-oblong, 1-3 cm × 2.5-4 mm, with almost no stalk. Leaf tips are rounded or blunt. Floral leaves are broader. Inflorescence is an inconspicuous terminal few-rayed cyathium. Flowers are borne inside a bell-shaped cone of bracts, within a pair of floral leaves. Flowering: May-September.
Dragon Spurge is an annual or short-lived perennial herb, growing to 10-40 cm tall. The species name dracunculoides means resembling a small dragon. Stem, 3-7 mm thick, are sometimes branched from below. Alternately arranged leaves are linearly-oblong, 1-3 cm × 2.5-4 mm, with almost no stalk. Leaf tips are rounded or blunt. Floral leaves are broader. Inflorescence is an inconspicuous terminal few-rayed cyathium. Flowers are borne inside a bell-shaped cone of bracts, within a pair of floral leaves. Flowering: May-September.Taxonomical Classification
Kingdom: Plantae - Plants
Subkingdom: Streptophyta
Superdivision: Spermatophyta - Seed plants
Division: Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants
Class: Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons
Family: Euphorbiaceae
Genus: Euphorbia
Species: Euphorbia dracunculoides
Allied species:
Euphorbia lanceolata, Tithymalus dracunculoidesVERNACULAR NAMES
Sanskrit: sankhini, saptala, satala, titali Carmasahva, CaramakasaEnglish: Dragon Spurge •
Hindi: Bamburi, Bumburi, Ban-bui-jayanti
Urdu: Thuhar
Telugu: tillakada, tillakaada
Bengali: Chagalpupti
Marathi: Khachar Dudhi •Nivadung
Oriya: Naagapheni, Siju, Saptala
Gujarathi: Satale
Tamil: tilla-kada
Malayalam: Chasma Lantha, Pathiri
Kannada: bilee kaddi, bili kaddi, bili kalli, mandaa mada
Punjabi: Kangi
Arabic: sudab
Chinese: 蒿状大戟 hao zhuang da ji
Definition
The botanical name Euphorbia derives from Euphorbos, the Greek physician of king Juba II of Numidia (52–50 BC – 23 AD), who married the daughter of Anthony and Cleopatra. Juba was a prolific writer on various subjects, including natural history.Synonyms
Synonyms in Ayurveda: sahadevi, jvarhara, ardhaprasadanaRasa: Kashaya Tikta
Guna: Laghu Ruksha Teeskhsna
Veerya: Sheetha
Vipaka: Katu
Karma: Kaphahara Pittahara
Euphorbia dracunculoides of family Euphorbiaceae is used by local practitioners in rheumatism, epilepsy, edema, snake bite, warts and also possesses diuretic and purgative effects
Harvesting:
Flowering and fruiting: August-DecemberPhytochemistry:
Glyco-alkaloid (Euphorbine).PHARMACOLOGY:
IMPORTANT FORMULATIONS –Parts used for medicinal purpose
Fruit, ,Dosage:
50 g. of the drug for decoction.Substitute:
In kerala and bengal Acacia concinna willd is used as SaptalaAdultrants:
Because of similar morphology of the dried aerial parts of E. drancunculoides to Ruta graveolens, it is sold or used clinically as replacement of R. graveolens for analgesic and inflammatory disorders; gout and arthritisControversy:
In kerala and bengal Acacia concinna willd is used as SaptalaCommercial value:
: Euphorbia dracunculoides L is available in market in raw form. It is used by people for the treatment of warts, snake bite and epilepsy.Morphology:
An ascending to erect, annual or short-lived perennial, 15–30 cm tall. Root terete, single, 30–40 cm × 3–8 mm. Stem sometimes branched basally, 3–7 mm thick, branches ascending, terete, glabrous in all parts. Leaves opposite on all the flowering parts, alternate on some of the lower parts of the stem and branches, sessile; stipules absent; leaf blade linear to linear-lanceolate, 1–3 cm × 2.5–4 mm, acute or obtuse, rounded in at the base, margin entire; lateral veins few, inconspicuous, at acute angle to midrib. Inflorescence an inconspicuous terminal few-rayed cyathium; primary invo-lucral leaves similar to normal leaves, primary rays ca. 3, robust and ascending, dichotomous; cyathophylls 2, similar to normal leaves. Cyathium sessile; involucre broadly campanulate, 2–3 × 3–5 mm, lobes rounded; glands 4, pale brown, crescent-shaped, apex 2-horned, horns light green. Male flowers many, not ex-serted from involucre. Female flower: ovary exserted from cup, smooth, glabrous; styles free, persistent; style arms 2-lobed. Fruiting peduncle ca. 3 mm; capsule subglobose, ca. 3.5 × 3.5 mm, smooth or obscurely reticulate, glabrous. Seeds ovoid- cylindric, ca. 2.5 × 1.5–2 mm, usually tuberculate-rugose, blackish-brown, with whitish network of thin ridges; caruncle 0.5 mm.Histology:
Root – Young root shows exfoliated, single layered epidermis; mature root shows thin walled cork, composed of 10-12 layers of rectangular cells; secondary cortex consists of 4- 6 layers of oval, elliptical, parenchymatous cells; oval to elongated elliptical thick walled, lignified cells with wide lumen; groups of stone cells and a few fibres present in this region; endoderm is and pericycle not distinct; secondary phloem composed of sieve elements and parenchyma; secondary xylem consists of vessels, fibres, tracheids and medullary rays; all elements thick-walled and lignified; fibres and vessels having simple pits; starch grains simple, rounded to oval, 2.75 n in dia; found scattered in phloem region; rarely a few oil globules also present.
Stem – Shows a single layered epidermis composed of thick-walled, flattended, tangentially elongated cells; older stem shows 4-5 layers of cork composed of thinwalled, rectangular, tangentially elongated and radially arranged cells; cortex composed of 4-5 layers of oval to rectangular, tangentially elongated elliptical, thin-walled parenchymatous cells; stone cells oval to elongated, elliptical, thick-walled lignified, with wide lumen present in this region; endodermis not distinct; pericycle represented by groups of lignified fibres; secondary phloem narrow, composed of sieve elements, phloem parenchyma and a few elongated laticiferous sacs; secondary xylem composed of vessels, fibres and tracheids, traversed by numerous xylem rays; all elements, thickwalled and lignified, vessels having simple pits; fibres elongated and aseptate; centre occupied by a pith, consisting of thick-walled, circular to oval, parenchymatous cells; some rounded, small laticiferous sacs present in peripheral pith cells, filled with yellowish-brown content; starch grains more abundant in phloem and pith region, simple, solitary or in groups, rounded to oval, measuring 5.5-19.25 n in diameter.
Leaf–
Midrib – shows slightly convex outline; epidermis single layered, covered externally with thick, striated cuticle; hypodermis consists of single layered collenchymatous cells towards lower side; vascular bundle collateral and surrounded by 4-6 layers of thinwalled, parenchymatous cells.
Lamina -shows slightly wavy outline; epidermis on either covered with thick cuticle; paracytic stomata present on both surfaces; mesophyll differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma; palisade single layered present on both sides; spongy parenchyma 4-5 layered consisting of irregularly arranged cells present between upper and lower palisade; a few small collateral vascular bundles embedded in spongy parenchyma.
Powder – Light yellow; shows vessels with simple pits, aseptate fibres; oval to elongated, elliptical, stone cells thick-walled, lignified with wide lumen; simple, rounded to oval starch grains, measuring 3-19 n in diameter.
Geographical distribution:
Plant conservation:
Not Evaluated (NE)General Use:
Fruit—removes warts topically. Plant extract—cholinergic. The aerial parts are used as a vegetable for maintaining smooth and regular movement of bowels.Therapeutic Uses:
Anaha, Gulma, Udararoga, Vibandha, Udavartta, Visarpa.Systemic Use:
Leaf juice is used to kill lice in human as well as in animal. Leaf paste is used to cure problems of head.Administration:
Euphorbia dracunculoides L is available in market in raw form.Pharmacological:
It is used by people for the treatment of warts, snake bite and epilepsy.Clinical trials:
Research:
Use in other system of medicine:
Euphorbia dracunculoides of family Euphorbiaceae is used by local practitioners in rheumatism, epilepsy, edema, snake bite, warts and also possesses diuretic and purgative effects.CONCLUSION:
Saptala consists of dried whole plant of Euphorbia dracunculoides Lam. (Fam. Euphorbiacem); a much branched, 20-40 cm high, annual herb, found throughout India in the plains and low hills Used in Anaha, Gulma, Udararoga, Vibandha, Udavartta, Visarpa.Photos of sahadevi -
Euphorbia dracunculoides
- Courtesy: https://08511630493324166816.googlegroups.com/attach/7474f9a04e500814/Euphorbia%20dracunculoides%20(1).JPG?part=0.2&view=1&vt=ANaJVrGqa9BHWyGWjBZvBKkLFWtxGlprqxrRpCZnXiIKA89OzXSJ2ssflgRWstt3wDF12nwdXp6svzqc3kgXm6G1Zpnw6xF4Zr_jZE18hBRxJnbHXy5qngQ
- Courtesy: https://08511630493324166816.googlegroups.com/attach/fdab194c35018841/tn_Euhorbia%20dracunculoides%20(5).JPG?part=0.1&view=1&vt=ANaJVrGVT6Kh-K0B7dEbiNuvpL31ZCfJ-CGroiYWpFW8zM1tIcyVeBJlBQC-4sX4x0IlKuCtnezGUeuDUg69uN9Ni786KIYustrCPakVTRiGYUkzOXu9qrs
- Courtesy: https://08511630493324166816.googlegroups.com/attach/7474f9a04e500814/Euphorbia%20dracunculoides%20(1).JPG?part=0.2&view=1&vt=ANaJVrGqa9BHWyGWjBZvBKkLFWtxGlprqxrRpCZnXiIKA89OzXSJ2ssflgRWstt3wDF12nwdXp6svzqc3kgXm6G1Zpnw6xF4Zr_jZE18hBRxJnbHXy5qngQ
- Courtesy: http://www.westafricanplants.senckenberg.de/images/pictures/euphorbia_dracunculoides-flamandii_ccc_3933cycha_9381_f96e16.jpg
- Courtesy: http://plantillustrations.org/illustration.php?id_illustration=162546&SID=0&mobile=0&code_category_taxon=9&size=1
KEY WORDS: sahadevi Euphorbia dracunculoides Lam.
- » Classification and names of sahadevi
- » Synonyms and definitions of sahadevi
- » Drug Properties of sahadevi
- » Chemical Constituents of sahadevi
- » Standardization of sahadevi
- » Parts used and Dosage of sahadevi
- » Morphology and Histology of sahadevi
- » Distribution and Conservation of sahadevi
- » Cultivation of sahadevi
- » sahadevi in the market
- » Medicinal Uses of sahadevi
- » Researches and clinical trails of sahadevi
- » sahadevi in other sytems of medicine
- » Ayurvedic formulations with sahadevi
- » Images of sahadevi

Kotakkal Ayurveda - Mother land of modern ayurveda